Debridement
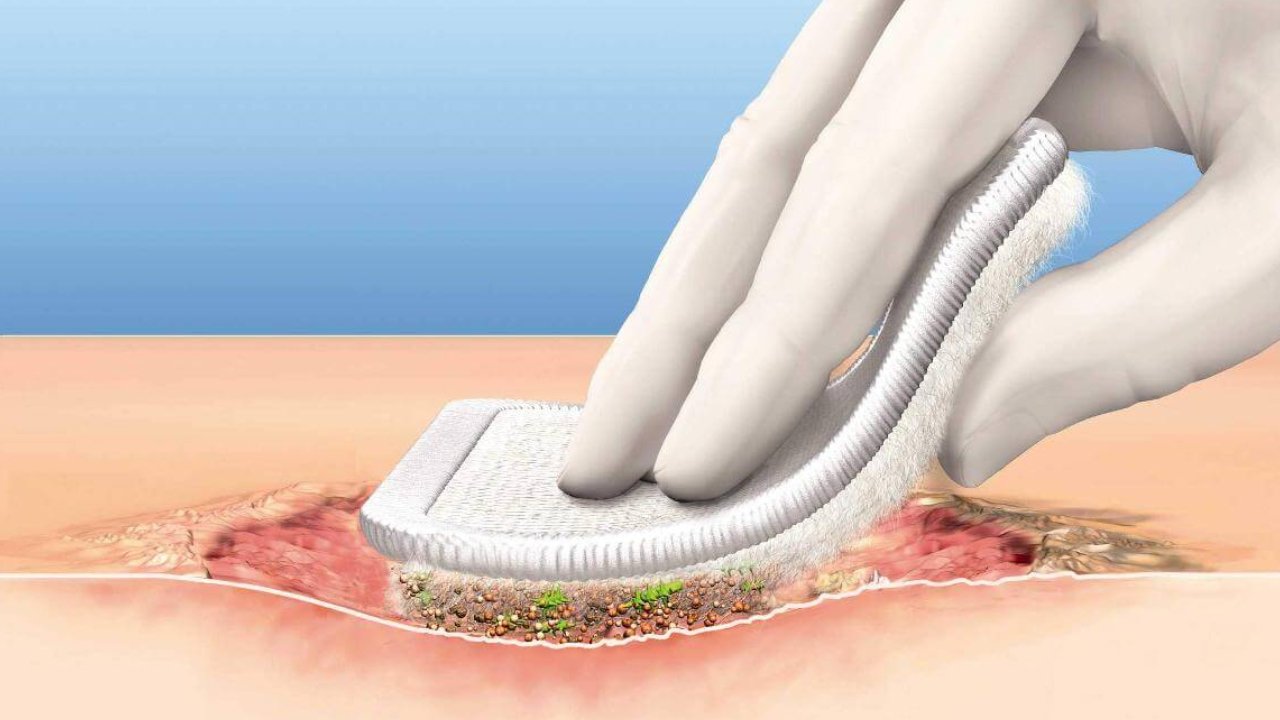
Introduction:
Debridement is a crucial medical procedure used to remove damaged or infected tissue from wounds or ulcers. It is essential for promoting proper healing, preventing infection, and reducing pain. In this blog, we will explore the different types of debridement, the conditions it is used for, and the treatments associated with it.
Types of Debridement
- Sharp Debridement: This is the most common form of debridement, performed by a healthcare professional using a scalpel, scissors, or a similar instrument. Sharp debridement is effective for removing thick or necrotic tissue from the wound, allowing for healthy tissue to regenerate.
- Mechanical Debridement: This method involves the use of mechanical forces, such as whirlpool therapy or wet-to-dry dressings, to physically remove dead or infected tissue. These techniques are particularly suitable for wounds with loose or moist necrotic tissue.
- Enzymatic Debridement: Enzymatic debridement utilizes topical enzymes, such as collagenase, to break down necrotic tissue. This is a less invasive option and is often used for wounds that are difficult to access or when sharp debridement may be too painful.
- Autolytic Debridement: Autolytic debridement relies on the body’s natural processes. It involves the application of occlusive dressings or hydrocolloid dressings that trap wound fluid. This fluid softens and loosens the necrotic tissue, allowing the body’s enzymes to naturally digest it.
Conditions Requiring Debridement:
- Chronic Wounds: Debridement is commonly used for chronic wounds like diabetic ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers. These wounds often develop necrotic tissue and benefit greatly from debridement to stimulate healing.
- Burns: Severe burns often require debridement to remove damaged skin and tissue, preventing infection and promoting the growth of healthy skin.
- Surgical Wounds: In cases where a surgical wound becomes infected or has delayed healing, debridement may be necessary to remove infected tissue and facilitate proper closure.
- Traumatic Wounds: Injuries resulting from accidents or trauma may lead to wounds with foreign debris or necrotic tissue, making debridement essential to prevent infection and support healing.
Treatment Process:
- Assessment: The first step is a thorough assessment of the wound’s type, size, and level of infection. This helps determine the appropriate debridement method.
- Pain Management: Local anesthesia or pain management techniques are often used to ensure the patient’s comfort during debridement.
- Debridement: Depending on the type of debridement chosen, the procedure is performed, aiming to remove all necrotic or infected tissue.
- Dressing Application: After debridement, a suitable wound dressing is applied to maintain a moist and sterile environment, supporting the healing process.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: The wound’s progress is closely monitored, and additional debridement sessions may be needed. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to track healing and make any necessary adjustments.
Conclusion:
Debridement is a critical medical procedure used to remove damaged or infected tissue from wounds, facilitating the body’s natural healing processes. Various types of debridement are available, each suited to different wound conditions. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate assessment and appropriate treatment plan when dealing with wounds requiring debridement. Prompt and effective debridement can significantly improve healing outcomes and quality of life for patients with these challenging conditions.
Contact Us
Get In Touch
Address
F 146/9 second floor shaheen bagh jamia Nagar New Delhi 110025
Phone
+91-9716952857
cure2world@gmail.com

