ACL Reconstruction: Restoring Stability to Injured Knees
Introduction:
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a vital structure in the knee, providing stability and support during various movements like running, jumping, and cutting. Unfortunately, ACL injuries are common, especially among athletes. When the ACL is torn or ruptured, it often requires surgical intervention called ACL reconstruction. ACL reconstruction is a surgical procedure aimed at restoring stability to the knee by replacing the damaged ACL with a graft.
Here’s a detailed overview of the process:
- Preparation: Before surgery, the patient undergoes a thorough evaluation, which includes a physical examination and imaging tests (e.g., MRI) to confirm the ACL tear’s severity and assess the overall knee health.
- Graft Selection: The surgeon and patient discuss graft options, which can be autografts (tissue from the patient’s own body) or allografts (donor tissue). Common autograft sources include the patellar tendon, hamstring tendons, or quadriceps tendon.
- Anesthesia: ACL reconstruction is typically performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is asleep and pain-free during the procedure.
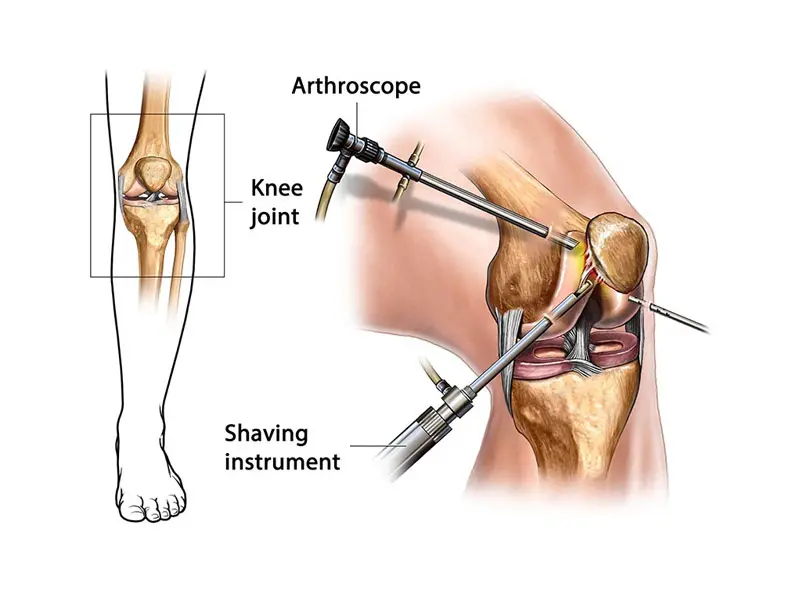
- Surgical Technique: Small incisions are made around the knee. The torn ACL is removed, and tunnels are drilled into the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia) to place the graft in a position that mimics the original ACL.
- Graft Placement: The chosen graft is inserted through the bone tunnels and secured with screws or other fixation devices.
- Rehabilitation: After surgery, patients begin a carefully planned rehabilitation program. Physical therapy focuses on regaining knee strength, range of motion, and stability. It typically involves exercises, bracing, and a gradual return to activities.
- Recovery: ACL reconstruction recovery can take several months. Patients may need to use crutches and a brace initially, gradually transitioning to normal activities as strength and stability improve.
- Return to Sports: Athletes may need a more extended recovery period, usually six to twelve months, before returning to competitive sports. The timing varies based on individual progress and the surgeon’s recommendations.
- Long-term Outlook: ACL reconstruction is highly successful in restoring knee stability and function. However, the risk of reinjury or the development of osteoarthritis later in life is a concern. Proper rehabilitation, ongoing strength training, and injury prevention strategies are crucial for maintaining knee health.
In conclusion, ACL reconstruction is a surgical procedure that restores stability to the knee after an ACL tear. It involves graft selection, surgical technique, and a comprehensive rehabilitation program. Although the recovery process may be challenging, the goal is to return patients to their desired level of activity with a stable and functional knee.

