Brain Aneurysm
Understanding Brain Aneurysm Surgery: Types and Treatment
Introduction:
A brain aneurysm is a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by a weak spot or bulge in a blood vessel within the brain. When left untreated, these aneurysms can rupture, leading to a potentially fatal brain hemorrhage. Fortunately, there are surgical options available to treat brain aneurysms. In this blog, we will delve into the different types of brain aneurysm surgery and their treatments.
Types of Brain Aneurysm Surgery:
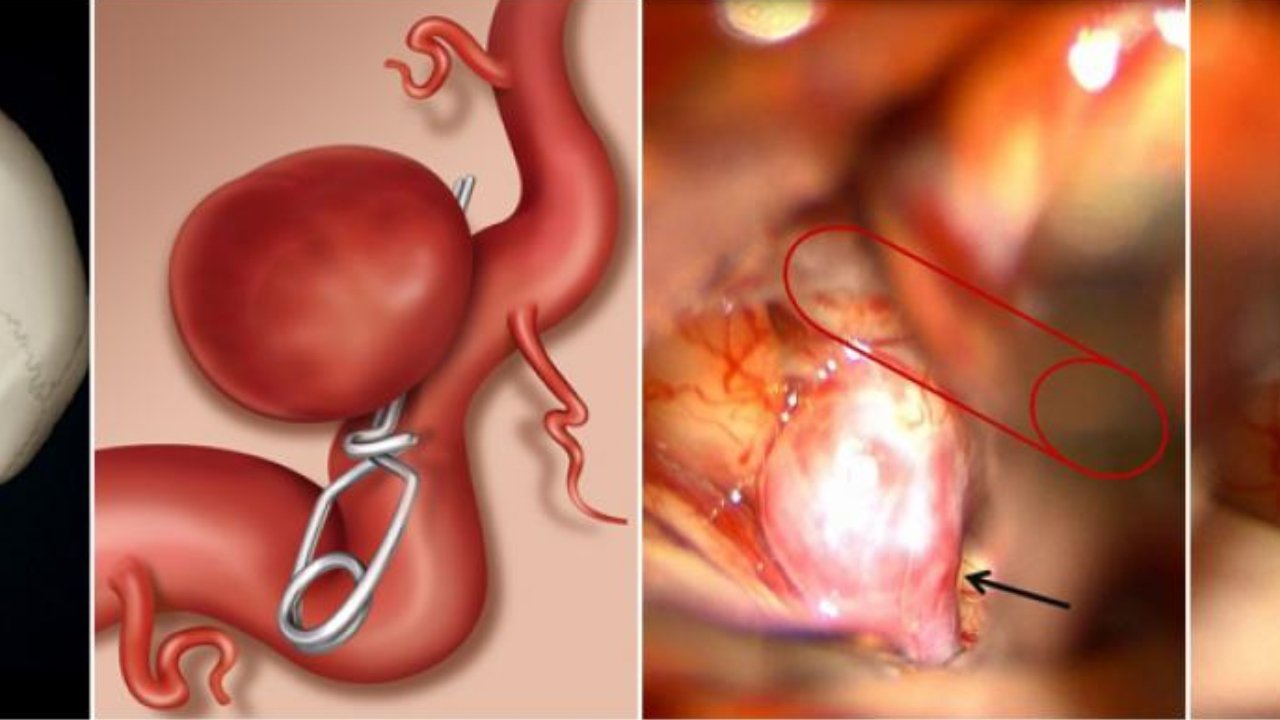
- Clipping Surgery: Clipping surgery, also known as surgical clipping or craniotomy, is one of the traditional methods to treat brain aneurysms. In this procedure, a neurosurgeon opens the skull to access the aneurysm directly. A small metal clip is then placed at the base of the aneurysm to prevent blood flow into it. Clipping surgery is highly effective and has a low risk of aneurysm recurrence.
- Endovascular Coiling: Endovascular coiling is a minimally invasive technique used to treat brain aneurysms. Instead of opening the skull, a neurointerventional radiologist inserts a catheter through an artery in the groin and threads it up to the aneurysm site. Soft platinum coils are then inserted into the aneurysm, causing it to clot and block blood flow. This procedure is less invasive than clipping surgery and often results in shorter recovery times.
- Flow Diverters: Flow diverters are a relatively newer option for treating brain aneurysms. They are stent-like devices that are placed across the neck of the aneurysm to redirect blood flow away from it. This promotes clotting and eventually seals off the aneurysm. Flow diverters are especially useful for complex or large aneurysms.
- Pipeline Embolization Device (PED): The PED is a specific type of flow diverter designed to treat wide-necked aneurysms. It is a fine mesh tube that is inserted into the parent artery to divert blood flow and promote aneurysm closure. This technique has shown promise in the treatment of challenging aneurysms.
Treatment Process:
- Diagnosis:A brain aneurysm is typically diagnosed through imaging tests like CT angiography or magnetic resonance angiography.
- Assessment:Once diagnosed, the size, location, and shape of the aneurysm are evaluated to determine the most suitable treatment approach.
- Surgical Procedure:Depending on the chosen method (clipping, coiling, flow diverters, or PED), the patient undergoes the respective surgical procedure. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including aneurysm characteristics and the patient’s overall health.
- Recovery:After surgery, patients will spend time in the hospital for observation. Recovery periods vary depending on the procedure but generally range from a few days to several weeks.
- Follow-Up:Regular follow-up appointments and imaging tests are essential to monitor the treated aneurysm’s stability and ensure there is no recurrence.
Conclusion:
Brain aneurysm surgery is a critical and potentially life-saving procedure that can prevent the rupture of aneurysms and minimize the risk of severe brain damage or death. The choice of surgery depends on various factors, including the aneurysm’s size, location, and the patient’s overall health. With advancements in medical technology, there are now multiple surgical options available, ranging from traditional clipping to minimally invasive techniques like endovascular coiling and flow diverters. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial in improving the prognosis for individuals with brain aneurysms, making it essential to be aware of the symptoms and seek medical attention promptly.
Contact Us
Get In Touch
Address
F 146/9 second floor shaheen bagh jamia Nagar New Delhi 110025
Phone
+91-9716952857
cure2world@gmail.com

