CATHETER ABLATION
Introduction:
Catheter ablation is a medical procedure that is commonly used to treat various heart rhythm disorders, also known as arrhythmias. This minimally invasive technique offers an effective solution for patients suffering from irregular heartbeats, helping to restore normal cardiac function and improve their quality of life.
The Procedure:
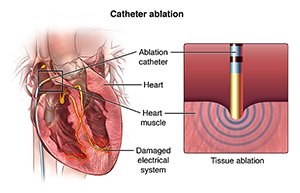
During catheter ablation, a specially trained cardiologist uses a thin, flexible tube called a catheter, which is inserted through a blood vessel, typically in the groin or wrist, and guided to the heart. The catheter is equipped with electrodes and sensors to map the electrical signals within the heart. These signals are crucial for maintaining a regular heartbeat.
Mapping and Targeting:
Once inside the heart, the catheter maps the abnormal electrical pathways or areas causing the arrhythmia. This precise mapping helps identify the specific location that needs to be treated. The goal is to eliminate or modify the abnormal tissue causing the erratic electrical signals.
Ablation:
After mapping, the ablation process begins. This involves delivering energy, such as radiofrequency or cryo-energy, through the catheter to the targeted tissue. This energy destroys or scars the problematic tissue responsible for the arrhythmia, effectively interrupting the abnormal electrical pathways.
Benefits of Catheter Ablation
- High Success Rate: Catheter ablation has a high success rate in treating various arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and supraventricular tachycardia.
- Minimally Invasive: Compared to traditional open-heart surgery, catheter ablation is minimally invasive, reducing the risks and complications associated with more invasive procedures.
- Improved Quality of Life: Successful ablation can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life by eliminating symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, and fatigue.
- Reduced Medication Dependence: Many patients can reduce or eliminate the need for long-term medications to control their arrhythmias after successful ablation.
- Quick Recovery: Recovery time for catheter ablation is typically short, and patients can often return to their normal activities within a few days.
Conclusion
Catheter ablation is a highly effective and minimally invasive procedure for treating heart rhythm disorders. By precisely targeting and eliminating the source of abnormal electrical signals in the heart, it offers patients a path to a healthier, more active life with fewer symptoms and reduced dependence on medications. If you are experiencing irregular heartbeats, consult with a cardiologist to determine if catheter ablation is an appropriate treatment option for you.

